As climate change and artificial intelligence (AI) reshape the world, some say that reality is starting to look a lot like science fiction. A book that people often point to is Kim Stanley Robinson’s The Ministry for the Future (2020).
The novel opens in 2025, with a deadly heatwave in India — a topic that turned out to be eerily prescient earlier this year, when the country faced extreme heat and humidity. In the book, the heatwave triggers a haphazard rallying of society to protect living creatures from climate catastrophe.
Robinson talked to Nature about how the climate crisis is causing younger generations anxiety, but also offering them existential meaning, and why he thinks that AI is a poor choice of name.
Why do you think The Ministry for the Future has garnered attention?
The novel is trying to say that, if we apply ourselves, we have the tools to avoid causing a mass-extinction event. And ordinary processes of humanity — science, diplomacy, treaties, the nation-state system, even capitalism itself — could be used to escape the crisis. That’s a very reassuring message.
Reducing personal climate risk to reduce personal climate anxiety
People are hungry for the feeling that everything could work out OK if we do things right. The book serves as a kind of encouragement, in the sense that it helps to give people courage.
At the same time, the start of the novel is so awful that it reproduces the feeling of climate dread. Really, I don’t even like to look at those pages again. But it gets to a better place. And as people read the book, they co-create it with me.
Reading a novel is an intensely creative act. You have to look at black marks on a page, and events appear in your head that can be as powerful as a real experience. If a passage has an emotional charge, it gets remembered as if it had really happened to you.
And how do you feel when events in your books actually happen?
I find it frightening and disturbing — but these were easy calls. I am no prophet.
If global average temperatures rise as much as they are expected to, there are going to be spikes in heat and humidity, and they will kill people. That was a finding by scientists looking at human adaptations to heat stress. They realized that the world might overcome our ability to shed excess heat by sweating when it’s humid. The idea was new in around 2010; I came across it in around 2017, after it was spread by attentive scientists and journalists.
What do you tell young people who worry about climate change?
I often talk to undergraduates about climate dread. They are the people of the future, because they’ll be here in 2075. Thinking about all the things that have to be accomplished by 2050 to avoid crossing tipping points into unavoidable catastrophe — of course you have climate dread.
The rise of eco-anxiety: scientists wake up to the mental-health toll of climate change
So I try to tell them that it means that your life has a project, you have existential meaning. You are not caught in the nihilism of meaninglessness that was capitalist realism. In the 1980s, you saw bumper stickers on US cars that said ‘he who dies with the most toys wins’. It was sarcasm, but it also pointed to a lack of meaning. Why live, what is it all about? Well, now we have that answered.
I also tell them: whatever you’re interested in, whatever your personal interests are, that can become climate work. Arts, public policy, psychology, the sciences, engineering, the humanities, they can all become part of climate work. Just find your angle. But, at the same time, acknowledge that we’re in an emergency, that something has to be done.
How do you research the science for your novels? It’s often realistic.
It’s cumulative — the research for one book adds knowledge to the next one. I probably read an hour or two of scientific journalism per day. That’s just out of curiosity, to try to keep up with what’s going on — and you can’t keep up. I read widely, but I’m behind the curve. The world is moving really fast.
You Might Also Like
Five ways increased militarization could change scientific careers
Ukrainian soldiers test drones in Donetsk, Febuary 2025.Credit: Serhii Mykhalchuk/Global Images Ukraine via GettyMilitary budgets are growing, especially in larger...
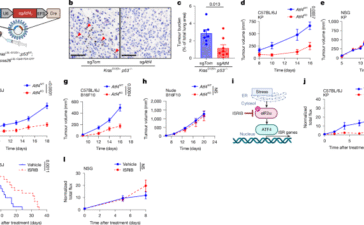
The integrated stress response promotes immune evasion through lipocalin 2
Cell linesThe KP cells used here were established previously66. Atf4 and Lcn2 knockout cell lines were generated by transient transfection...
How AI slop is causing a crisis in computer science
AI slop is flooding computer science journals and conferences.Credit: Quality Stock/AlamyFifty-four seconds. That’s how long it took Raphael Wimmer to...
The ‘astounding’ rise of semaglutide — and what’s next for weight-loss drugs
First established as a treatment for diabetes, semaglutide’s popularity as a weight-loss drug has opened the door to new therapies.Credit:...