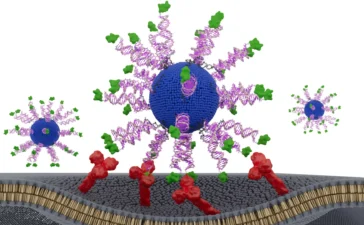
Investigators at Mass General Brigham have uncovered how resistance to chemotherapies may occur in some cancers. Researchers focused on a pathway that harnesses reactive oxygen species (ROS) to kill cancer cells. The study found that mutations to VPS35, a key player in this pathway, can prevent chemotherapy-induced cell death. These results, published in Nature, could help pinpoint treatment-resistant tumors.
“ROS play an important role in healthy and diseased cells, but pathways that sense and control cellular ROS levels are not well understood,” said corresponding author Liron Bar-Peled, PhD, of the Krantz Family Center for Cancer Research at Mass General Cancer Center (MGCC), a member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system. “A clearer understanding of ROS could help us understand why chemoresistance occurs in some cases.”
Low concentrations of ROS are required for normal cell signaling, but higher levels of ROS can damage cells and contribute to diseases such as cancer and neurodegeneration. Researchers know that mitochondria play an important role in ROS production, but it has been unclear if ROS-sensing proteins influence the mitochondria. If they do, this could impact responses to some anti-cancer treatments.
To investigate, co-first authors Junbing Zhang, PhD, Yousuf Ali, PhD, and Harrison Chong, of the Krantz Family Center for Cancer Research, and colleagues screened cancer cells for ROS-sensing proteins that might contribute to chemoresistance. The screen identified mutations that increased treatment resistance, and the team traced two of them to a protein called VPS35. Through further studies, they found that these mutations led to lowered ROS levels within the cell.
In addition, the investigators analyzed VPS35 expression levels in 24 patients with high grade serous ovarian cancer (HGSOC), who received treatment at MGCC. They noted that higher tumoral VPS35 levels were associated with improved treatment responses and with overall survival rates.
You Might Also Like
This reengineered HPV vaccine trains T cells to hunt down cancer
Over the last decade, scientists at Northwestern University have identified a key insight about how vaccines work. The ingredients matter,...
This planet friendly diet could cut your risk of early death by 23%
New research from Aarhus University suggests that the updated Nordic dietary guidelines, created to support both personal health and environmental...
Scientists discover protein that rejuvenates aging brain cells
Scientists at the Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine at the National University of Singapore have identified a protein that...
Scientists were wrong for decades about DNA knots
Scientists at the University of Cambridge, working with international collaborators, have identified a crucial process that shapes how DNA behaves...